
Understanding Thyroid Health: Conditions, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Expert Endocrine Care at Your Convenience.
Search and schedule at a location near you.
Thyroid disorders may affect nearly every aspect of your health, from how your body uses energy to your mood and heart rate. If you’ve noticed changes in your energy, weight, or mood, it’s important to connect with your trusted healthcare provider for an assessment – and if it turns out to be a thyroid disorder, learning about this tiny but important gland is a vital step toward better health.

What Is the Thyroid, and What Does It Do?
The thyroid is a gland located at the base of your neck. It produces thyroid hormone T4 (thyroxine). Thyroid hormone regulates how your body converts food into energy (metabolism), control your heart rate, and support brain and digestive function.
To maintain balance, the thyroid works in coordination with the pituitary gland, which releases TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) to signal when more or less thyroid hormone is needed. When this system is disrupted, it may lead to thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Common Thyroid Disorders and Symptoms
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid doesn’t produce enough hormones, slowing many of the body’s processes. Symptoms include:
- Persistent fatigue
- Weight gain
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Constipation
- Hair thinning or dry skin
- Depression or mental fog
Common causes:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid.
- Iodine Deficiency: Rare in the U.S. due to iodized salt but still a global cause of hypothyroidism.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as lithium, may affect thyroid function.
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Hyperthyroidism happens when the thyroid overproduces hormones, causing the body to function too quickly. Symptoms include:
- Anxiety, nervousness, or irritability
- Unintended weight loss despite normal eating habits
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Tremors or shaking hands
- Heat intolerance or excessive sweating
Common causes:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune disorder that overstimulates the thyroid.
- Toxic thyroid nodules: Overactive lumps in the thyroid that produce excess hormones.
- Excess iodine: From supplements, medications, or diet.
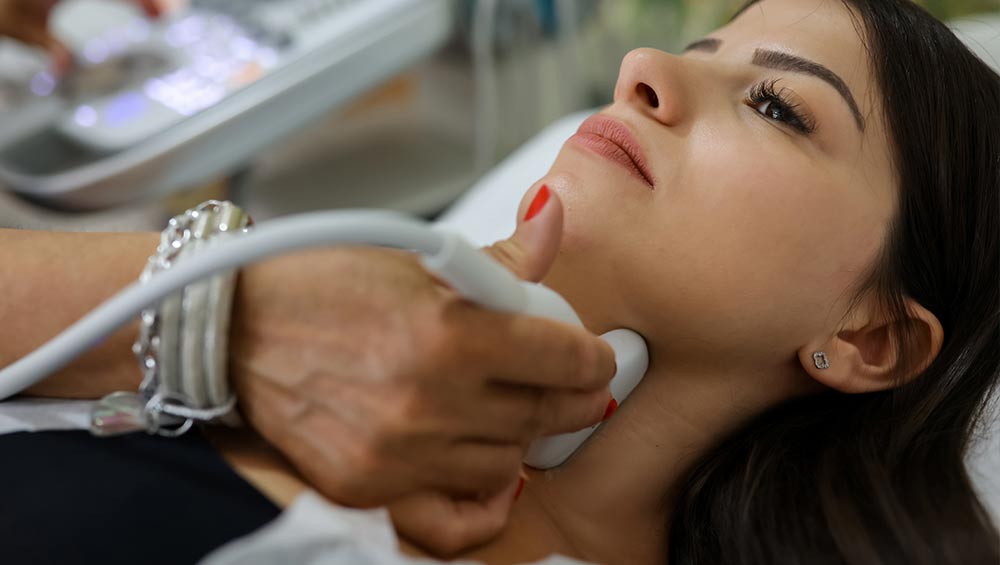
How Are Thyroid Disorders Diagnosed?
Typically, diagnosing thyroid disorders begins with a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
- Assessment: A medical provider, like your primary care doctor, can assess your thyroid and determine what next steps make the most sense based on your assessment.
- Blood tests: Measuring TSH, and T4 levels help determine if the thyroid is underactive, overactive, or functioning normally.
- Imaging: An ultrasound may be used to assess the size and structure of the thyroid or identify nodules.
- Thyroid scan: In some cases, radioactive iodine uptake tests help evaluate thyroid function.
Effective Treatments for Thyroid Disorders
For Hypothyroidism:
The primary treatment is levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4 that replaces the hormones your thyroid isn’t producing. It is taken daily and monitored regularly for accurate dosage.
For Hyperthyroidism:
- Antithyroid medications: Drugs like methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU) reduce hormone production.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment safely shrinks the thyroid by limiting its hormone production.
- Surgery: In rare cases, a thyroidectomy (removal of part or all of the gland) may be necessary.
Your individual treatment plan will depend on the specific cause of your thyroid condition, its severity, and your overall health.
Supporting Your Thyroid Health: Tips for Everyday Care
While thyroid disorders often require medical treatment, you can take steps to support thyroid function and overall wellness:
- Manage stress: Stress may interfere with hormone production. Practices like yoga, meditation, or walking may help maintain balance.
- Schedule regular checkups: Routine blood tests may detect thyroid problems early — even before symptoms develop.
The Kelsey-Seybold Difference: Comprehensive and Coordinated Care
At Kelsey-Seybold Clinic, we prioritize a coordinated care model with seamless communication between your primary care doctor, endocrinology specialist, and any additional specialists you may need. This collaborative approach allows us to create a personalized treatment plan that addresses all aspects of your thyroid health and how it affects your health overall.
Don’t wait to get the answers you need. Contact Kelsey-Seybold today to schedule a thyroid evaluation with your primary care provider or one of our board-certified endocrinologists.









